Central Rod Domain Lamin

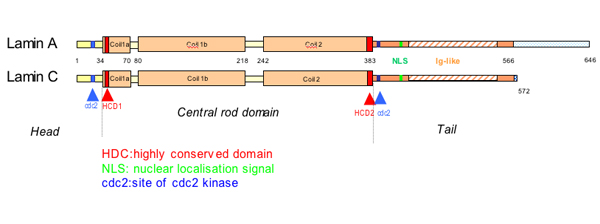
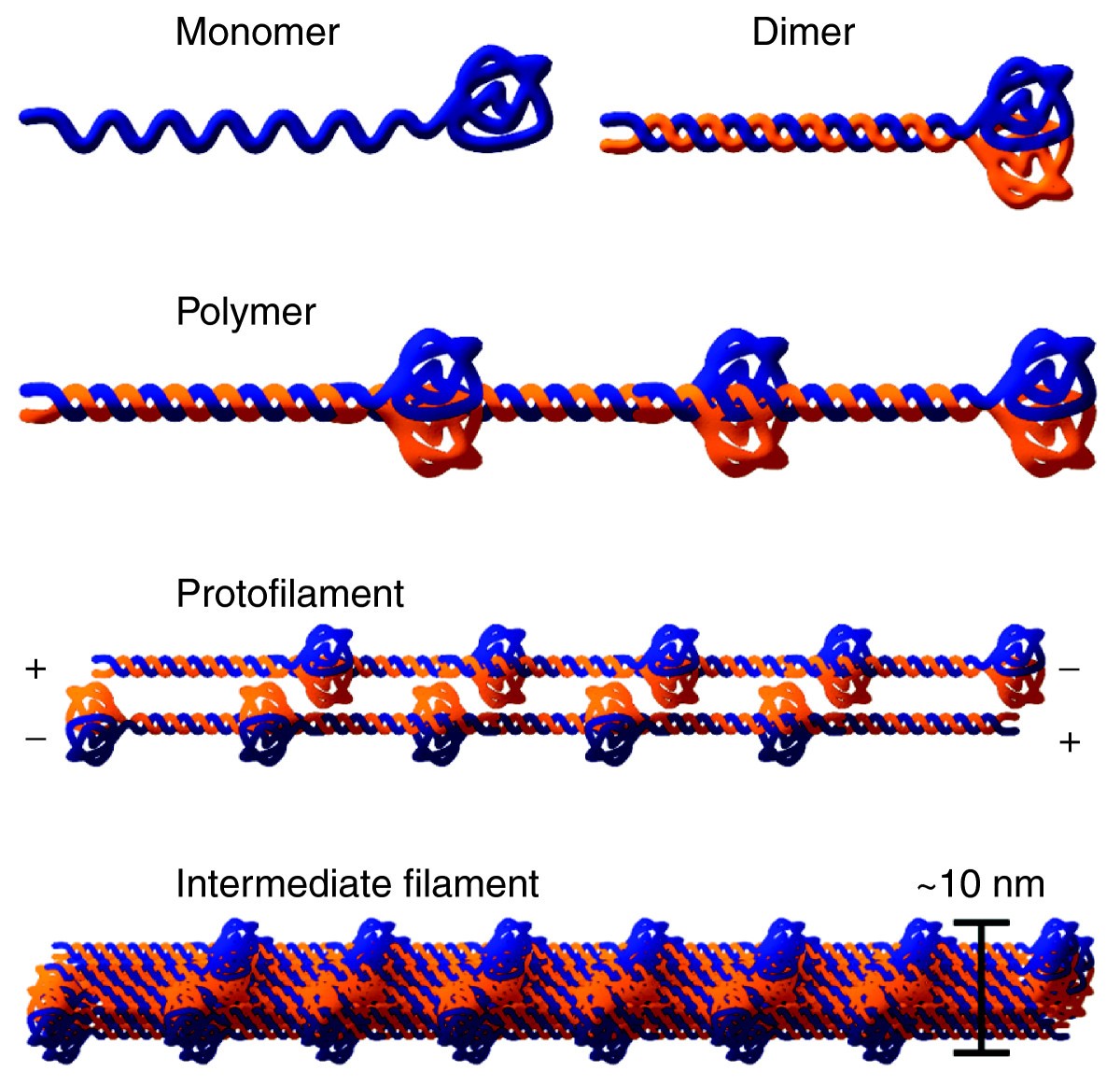
The lamins have a conserved central helical rod domain flanked by globular head and tail domains.
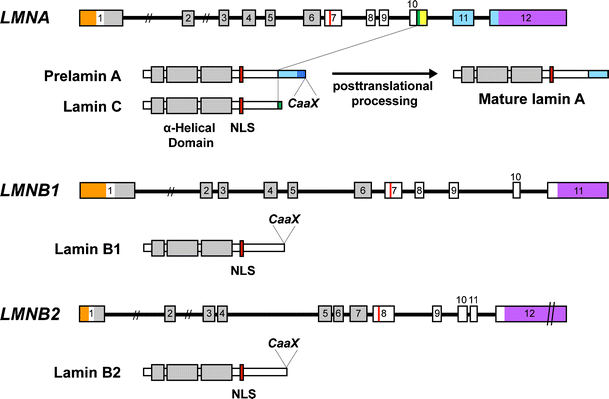
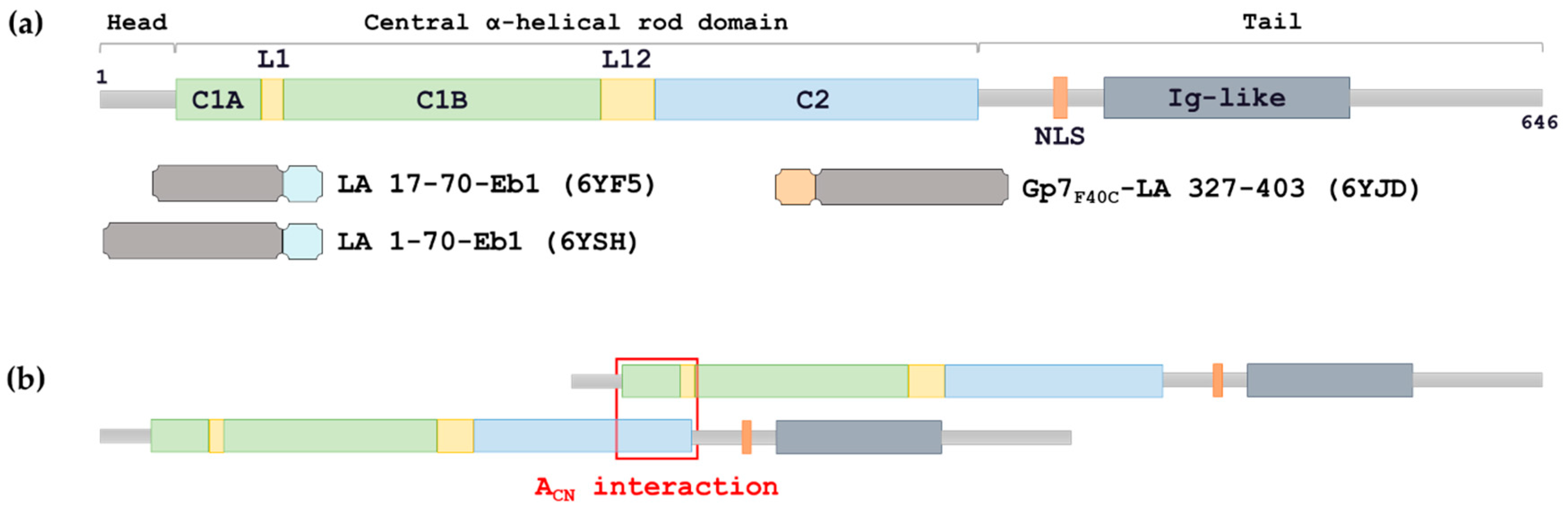
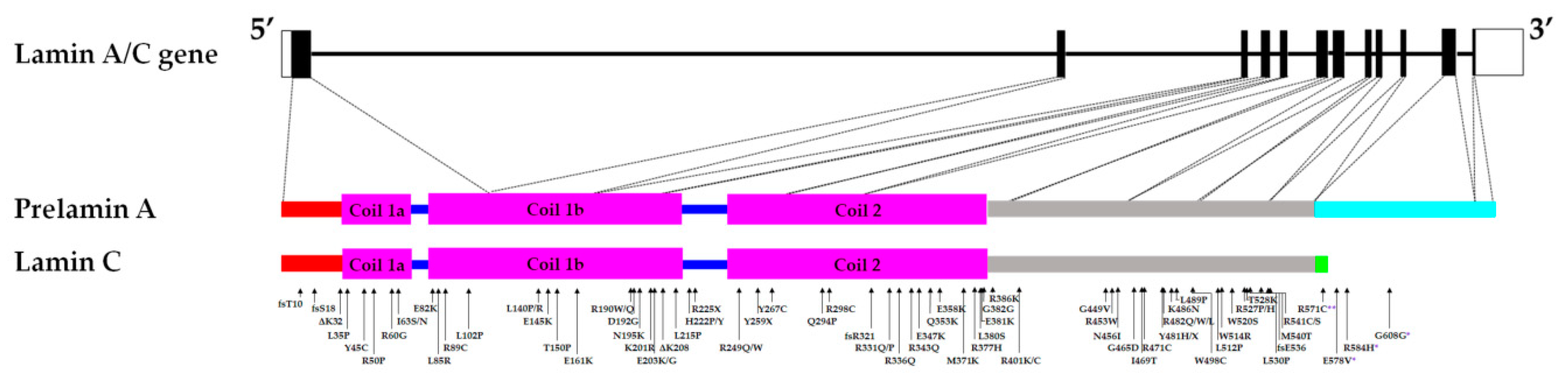
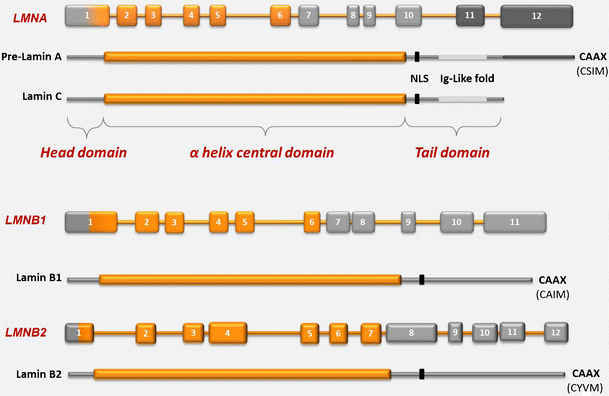
Central rod domain lamin. Exon 1 codes for the n terminal head domain and the first portion of the central rod domain exons 2 through 6 the central rod domain and exons 7 through 11 the c terminal tail domain. As suggested by the first model all if proteins appear to have a central alpha helical rod domain that is composed of four alpha helical segments named as 1a 1b 2a and 2b separated by three linker regions. We examined regions of human lamins a and c involved in binding to surfaces of mitotic chromosomes. Lamins consist of an n terminal head domain a coiled coil central rod domain and a globular c terminal tail domain containing an immunoglobulin ig like fold which in vitro binds nucleosomes.
The central α helical or rod domain spans approximately half of the lamin molecule about 350 residues and comprises four α helical segments termed 1a 1b 2a and 2b. An escherichia coli expression system was used to produce full length lamin a and lamin c and truncated lamins retaining the central alpha helical rod domain residues 34 388 but lacking various amounts of the amino terminal head and carboxy terminal tail domains. In vitro lamin dimers form head to tail chains which further. Some of these are located in the α helical central rod domain required for the polymerization of the nuclear lamins into higher order structures.
Numerous mutations in the human a type lamin gene lmna cause the premature aging disease progeria. The central building block of an intermediate filament is a pair of two intertwined proteins that is called a coiled coil structure. Each α helical segment has heptad repeat periodicity characteristic of coiled coil proteins and is connected by short intervening sub domains denoted l1 l12 and l2. Intron positions are conserved in other lamin genes from frogs mice and humans but different in lamin genes from drosophila and c.
The central rod is responsible for the formation of in parallel and in register coiled coil dimers the building blocks of lamin polymers. Patient cells with a mutation in this domain 433g a e145k show severely lobulated nuclei a separation of the a and b type lamins. An escherichia coli expression system was used to produce full length lamin a and lamin c and truncated lamins retaining the central alpha helical rod domain residues 34 388 but lacking various amounts of the amino terminal head and carboxy terminal tail domains. 24 it is reported in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy with atrioventricular block 25 and more recently in a family with dilated cardiomyopathy and lv non compaction.