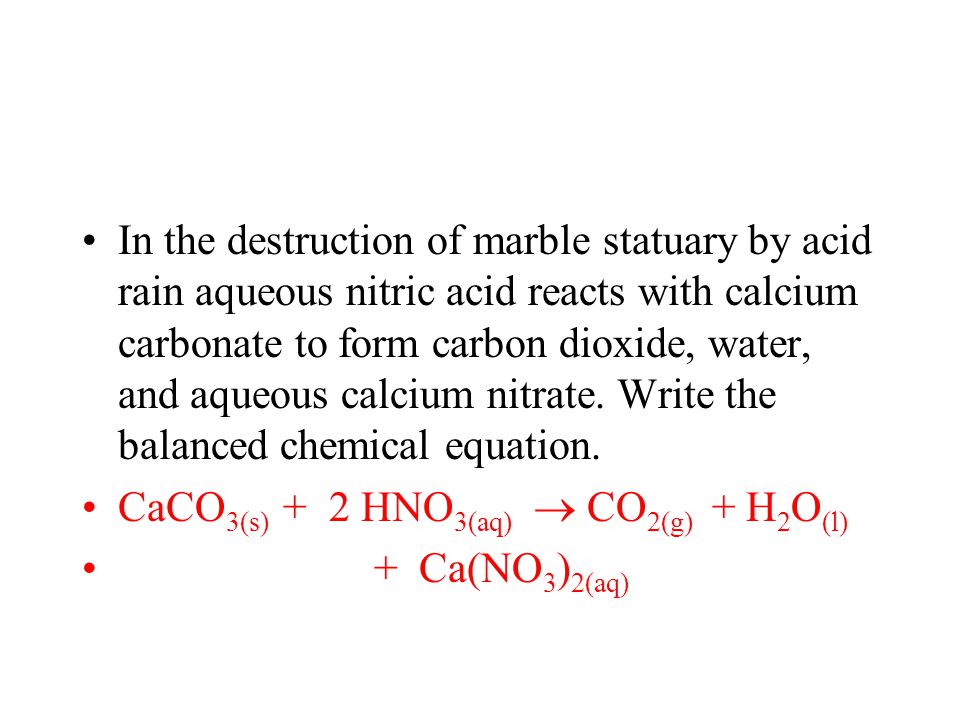Chemical Formula For Acid Rain And Marble

When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves.
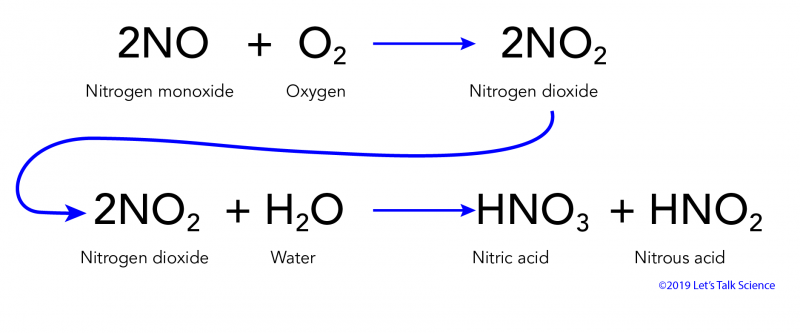
Chemical formula for acid rain and marble. A chemical reaction equation 9 between calcium carbonate and sulfuric acid the primary acid component of acid rain results in the dissolution of caco. Both marble and limestone consist of caco 3 which reacts with acid rain in an acid base reaction to produce caso 4. Acid rain acid rain chemistry of acid deposition. Acid rain is a rain or any other form of precipitation that is unusually acidic meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions low ph it can have harmful effects on plants aquatic animals and infrastructure.
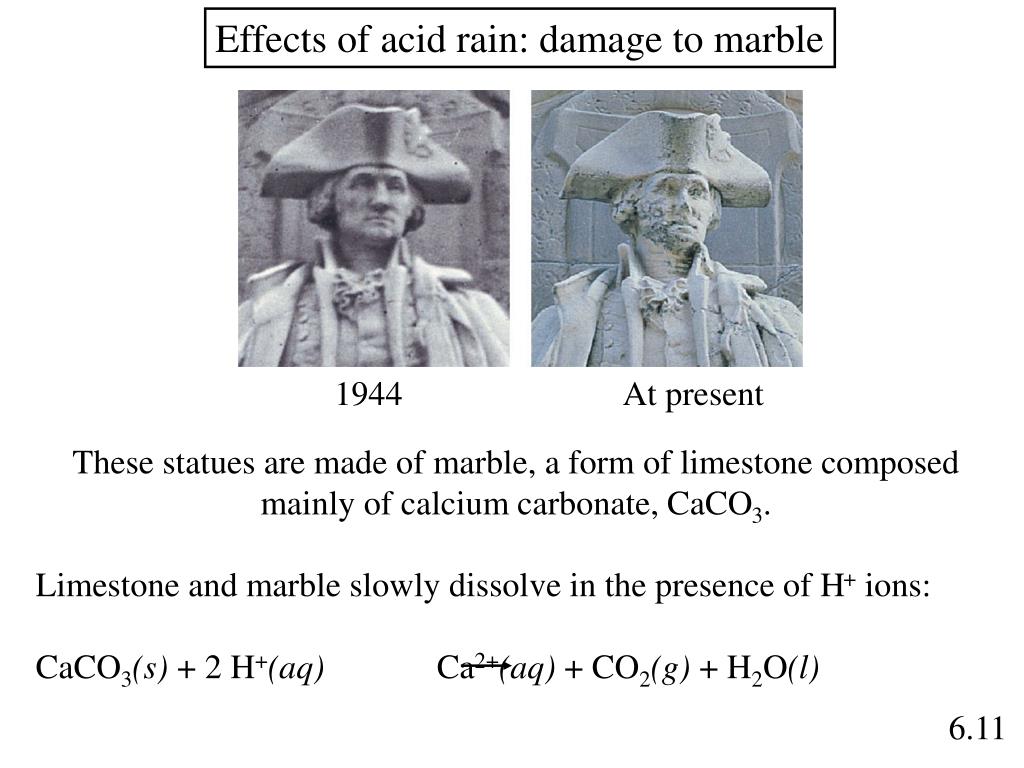
Students know how to use the ph scale to characterize acid and base solutions. In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened surfaces removal of material and loss of carved details. Because caso 4 is somewhat soluble in water significant damage to the structure can result. The marble will begin breaking down as a result of the acid.
Students know buffers stabilize ph in acid base reactions. Acid rain is a popular expression for the more scientific term acid deposition which refers to the many ways in which acidity can move from the atmosphere to earth s surface. Unlike granite marble can t take chemical weathering such as acid rain or any type of acid. Stone surface material may be lost all over or only in spots that are more reactive.
What effect does acid rain have on marble. Acid rain damage to a statue of george washington. The biological effects of acid rain are more complex. While marble is a strong material there are some conditions that it cannot stand.
Limonite will give marble a yellow color and serpentine will give marble a green color. When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air and rain react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves. However since the onset of acid rain these materials are at risk from erosion. Acid rain contains sulfuric acid which reacts with calcium carbonate to create aqueous ions.
Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Acid precipitation affects stone primarily in two ways. Both marble and limestone consist of caco 3 which reacts with acid rain in an acid base reaction to produce caso 4. How does acid precipitation affect marble and limestone buildings.
Because caso 4 is somewhat soluble in water significant damage to the structure can result. Acid deposition includes acidic rain as well as other forms of acidic wet deposition such as snow sleet hail and fog or cloud water. How does this happen. Although these are recognized as highly durable materials buildings and outdoor monuments made of marble and limestone are now being gradually eroded away by acid rain.